Which Abnormality Helps Identify Lung Tissue Disease
Which abnormality helps identify lung tissue disease. Respiratory distress from lung tissue disease - crackles. Acute respiratory distress syndrome ARDS is a rapidly progressive disease occurring in critically ill patients. 1st Lymphoid tissue cells form specific IgE antibodies after initial exposure to a certain.
2nd IgE antibodies attach themselves to mast cells. UIP presents histopathologic and radiologic evidence of heterogeneous patterns of patchy fibrotic scarring and honeycombing alternating with normal lung tissue. Brain lung or other tissues and G.
To determine the cause of interstitial lung disease a physician may perform a physical examination and order diagnostic tests including. The so-called Schamroth window test helps to identify. Lamblia microsporidia and Entamoeba histolytica in imprints of gastrointestinal biopsy.
Most people who get ARDS are already in the hospital for trauma or illness. Once you have spotted asymmetry the next step is to decide which side is abnormal. A blood clot usually in a deep leg vein called deep vein thrombosis breaks off travels to your heart and gets pumped into.
A chest x ray can help rule out other lung diseases as the cause of your childs symptoms. 3rd Re-exposure to the same antigen creates an antigen-antibody reaction on the surface of. Pulmonary embolism PE.
Cystic adenomatoid malformation of the lung is a developmental abnormality arising from an overgrowth of the terminal respiratory bronchioles. Rhythm - bradycardia no pulse - pulseless electrical activity. An HRCT scan uses x rays to create detailed pictures of your childs lungs.
These tests may help identify autoimmune diseases such as scleroderma and rheumatoid arthritis which can be associated with interstitial lung disease. Since it was established CTSN has developed a portfolio of trials spanning from early translation to the completion of six randomized clinical trials and three large observational studies.
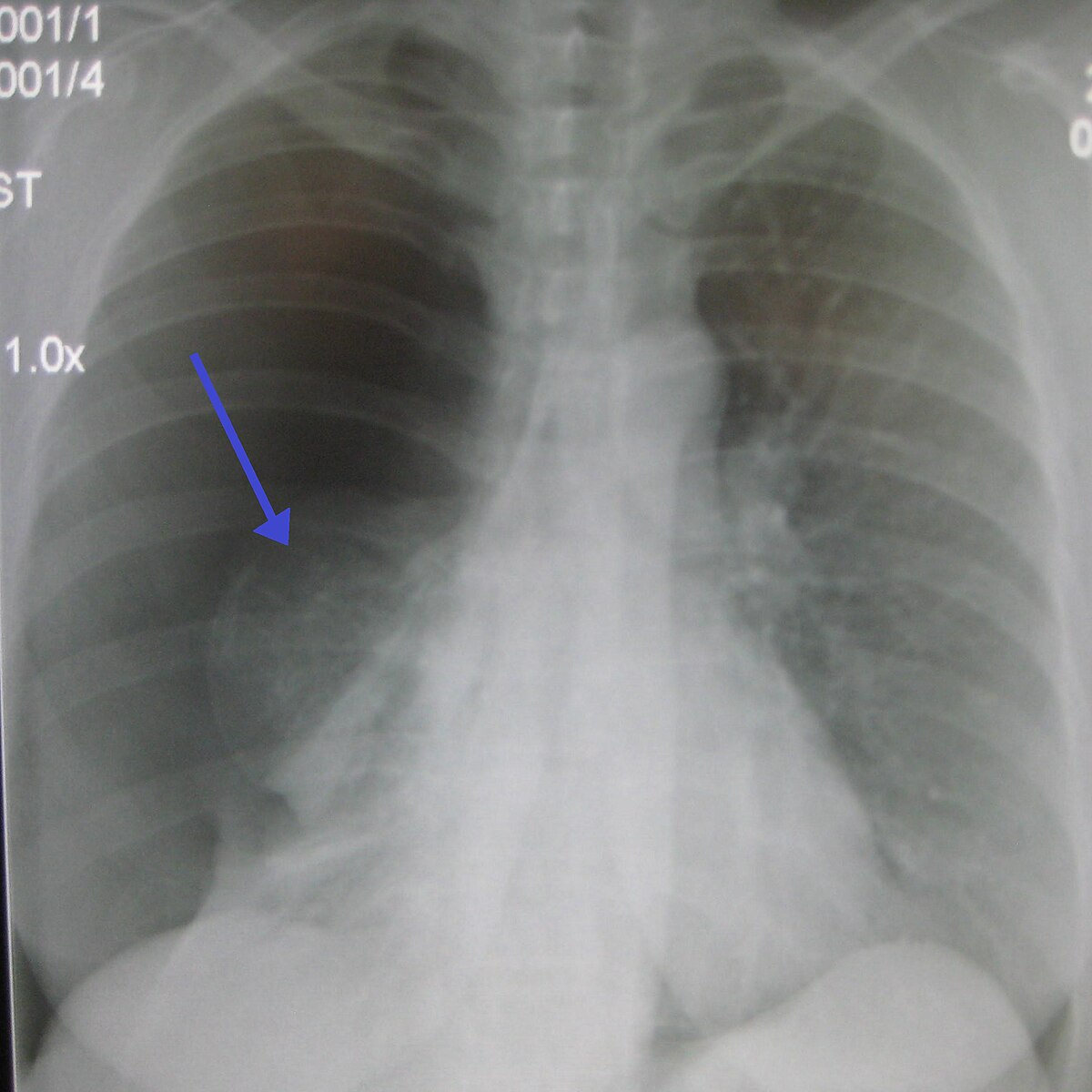
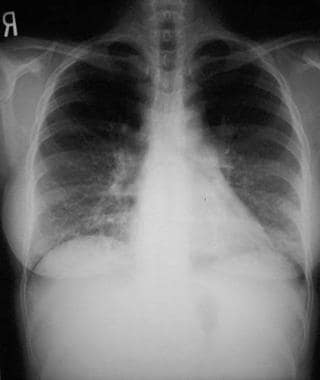
The condition may be bilateral involving all lung tissue but in the majority of cases it is confined to a single lung or lobe.
Once you have spotted asymmetry the next step is to decide which side is abnormal. Lamblia microsporidia and Entamoeba histolytica in imprints of gastrointestinal biopsy. To determine the cause of interstitial lung disease a physician may perform a physical examination and order diagnostic tests including. The condition may be bilateral involving all lung tissue but in the majority of cases it is confined to a single lung or lobe. Aside from demonstrating evidence of bronchiolar disease HRCT of the chest helps identify those cases in which an interstitial lung disease or large airway disease may be the predominant underlying process. Describe in order the sequence of events associated with the Immunologic Mechanism. Pulmonary embolism PE. Moist crackles rales indicate accumulated alveolar fluid dt lung tissue disease PNA or pulmonary edema or interstitial lung disease. The so-called Schamroth window test helps to identify.
A blood clot usually in a deep leg vein called deep vein thrombosis breaks off travels to your heart and gets pumped into. Once you have spotted asymmetry the next step is to decide which side is abnormal. The condition may be bilateral involving all lung tissue but in the majority of cases it is confined to a single lung or lobe. A chest x ray can help rule out other lung diseases as the cause of your childs symptoms. Lamblia microsporidia and Entamoeba histolytica in imprints of gastrointestinal biopsy. Acute respiratory distress syndrome ARDS is a rapidly progressive disease occurring in critically ill patients. 3rd Re-exposure to the same antigen creates an antigen-antibody reaction on the surface of.




























/lung-mass-possible-causes-and-what-to-expect-2249388-5bc3f847c9e77c00512dc818.png)










Post a Comment for "Which Abnormality Helps Identify Lung Tissue Disease"