Incomplete Kawasaki Disease Criteria
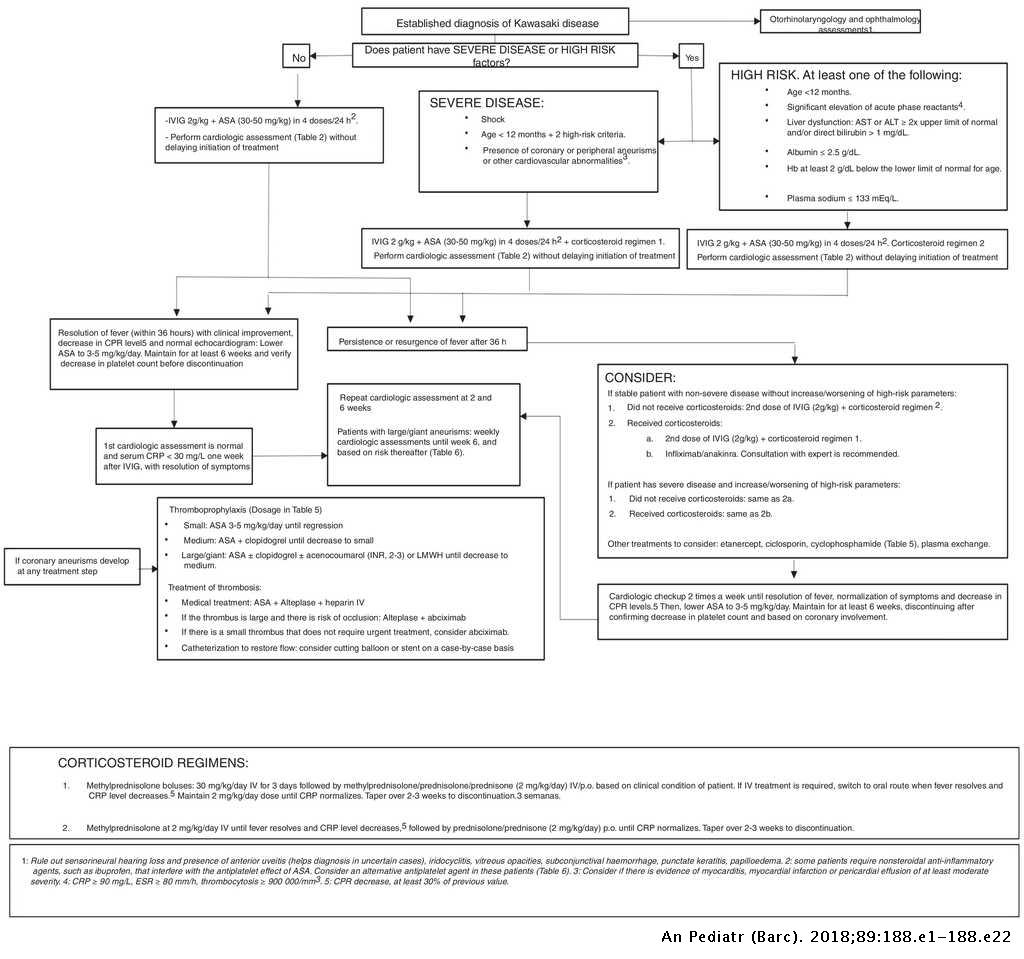
Incomplete kawasaki disease criteria. Kawasaki Disease is defined as fever for 5 days plus at least 4 out of 5 clinical features. Inflammatory labs supplemental labs and ECHO may be used to help guide management. A 3-month-old infant presented with severe KD 27 days after onset of fever.
Incomplete Kawasaki disease The presence of coronary artery abnormalities has been used as criterion for the diagnosis of incomplete Kawasaki disease26. Awasaki disease KD is an acute self-limited fe-brile illness of unknown cause that predominantly affects children. While the child has an incomplete set of criteria heshe has as the same risk for developing coronary artery aneurysms.
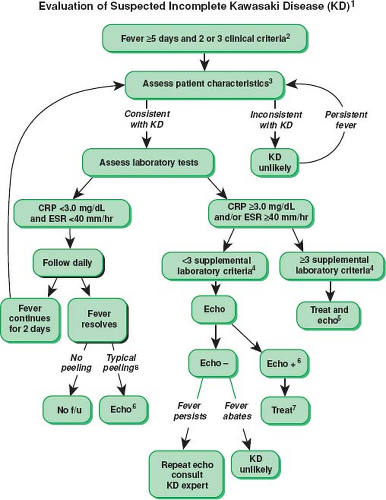
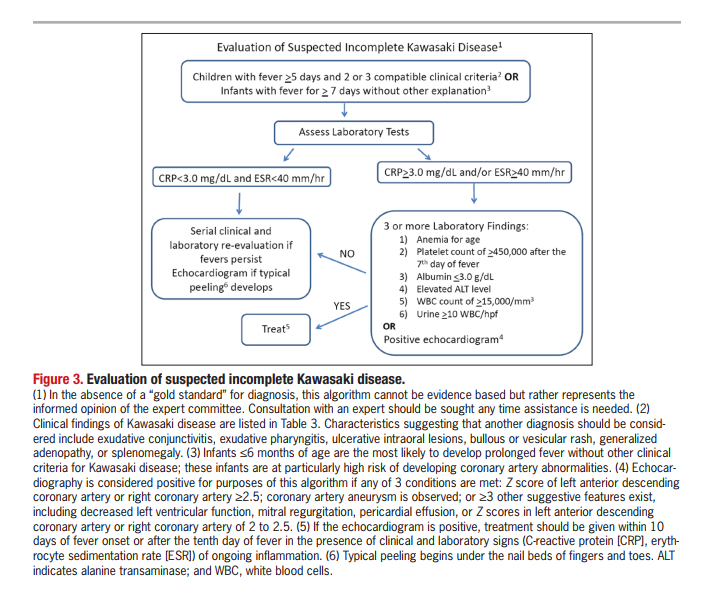
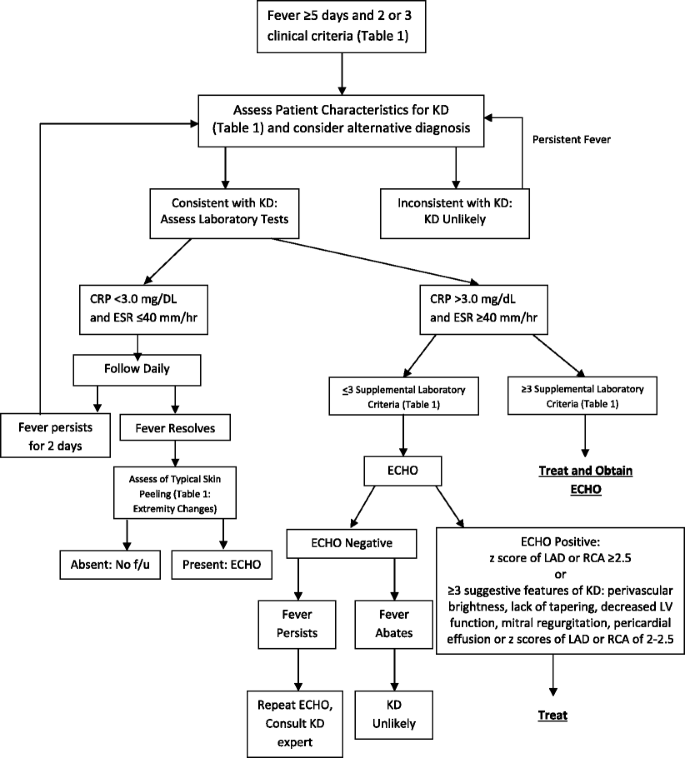
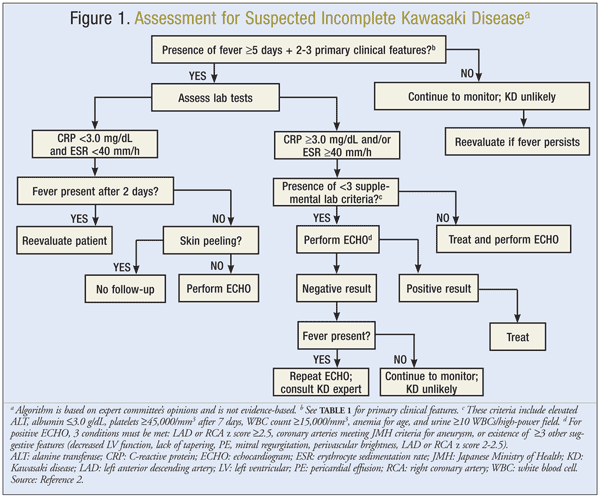
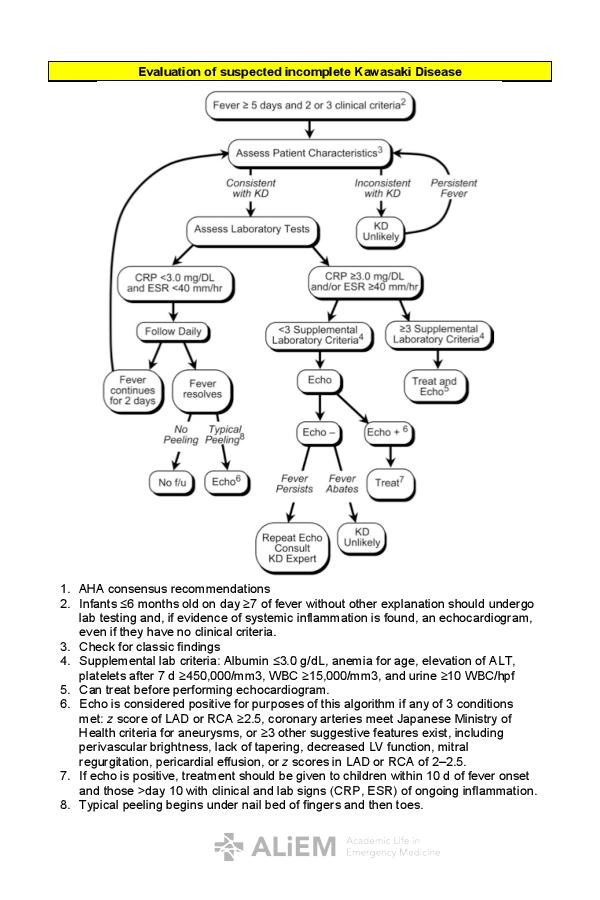
Consider lab testing if 3 days of fever and strong clinical suspicion for KD. Incomplete Kawasaki Disease The child has prolonged fever but only 2 or 3 of the characteristic features so not a complete complement of criteria. KD is now the most common cause of acquired heart disease in children in developed countries.
Cervical adenopathy 15 cm diameter OR. Bilateral conjunctival injection 2. Kawasaki disease KD is a clinical diagnosis that requires prompt recognition and management.
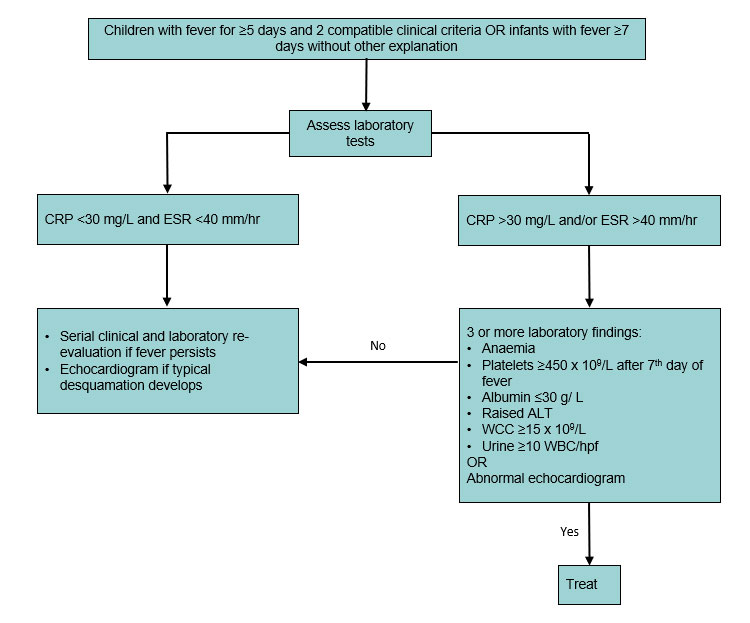
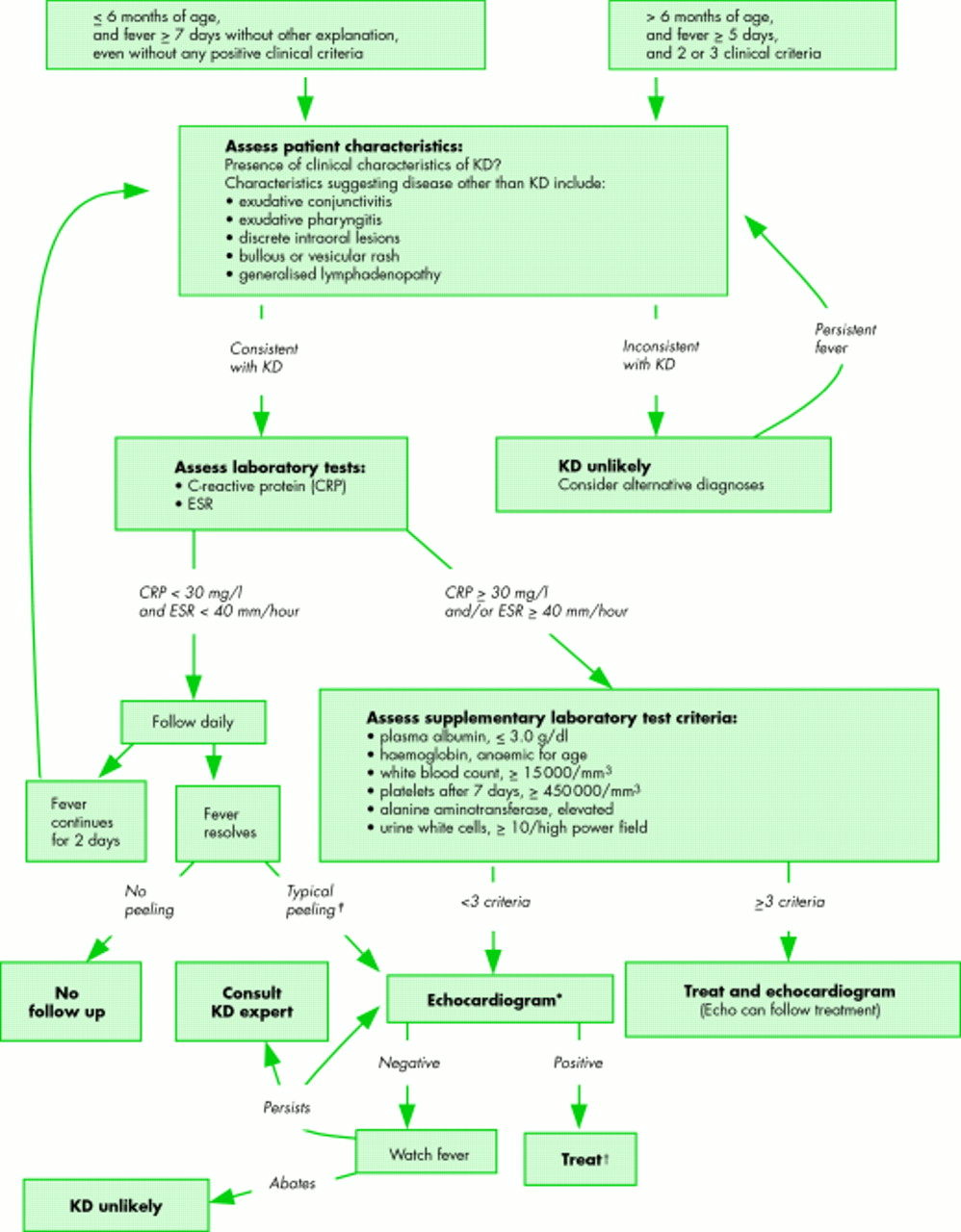
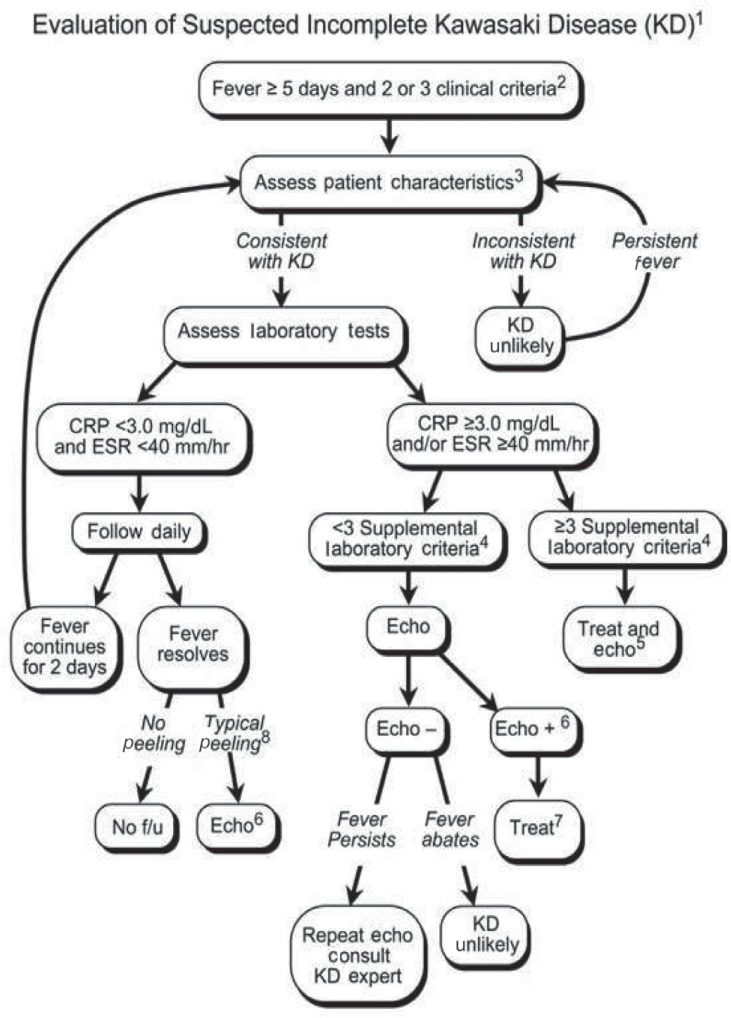
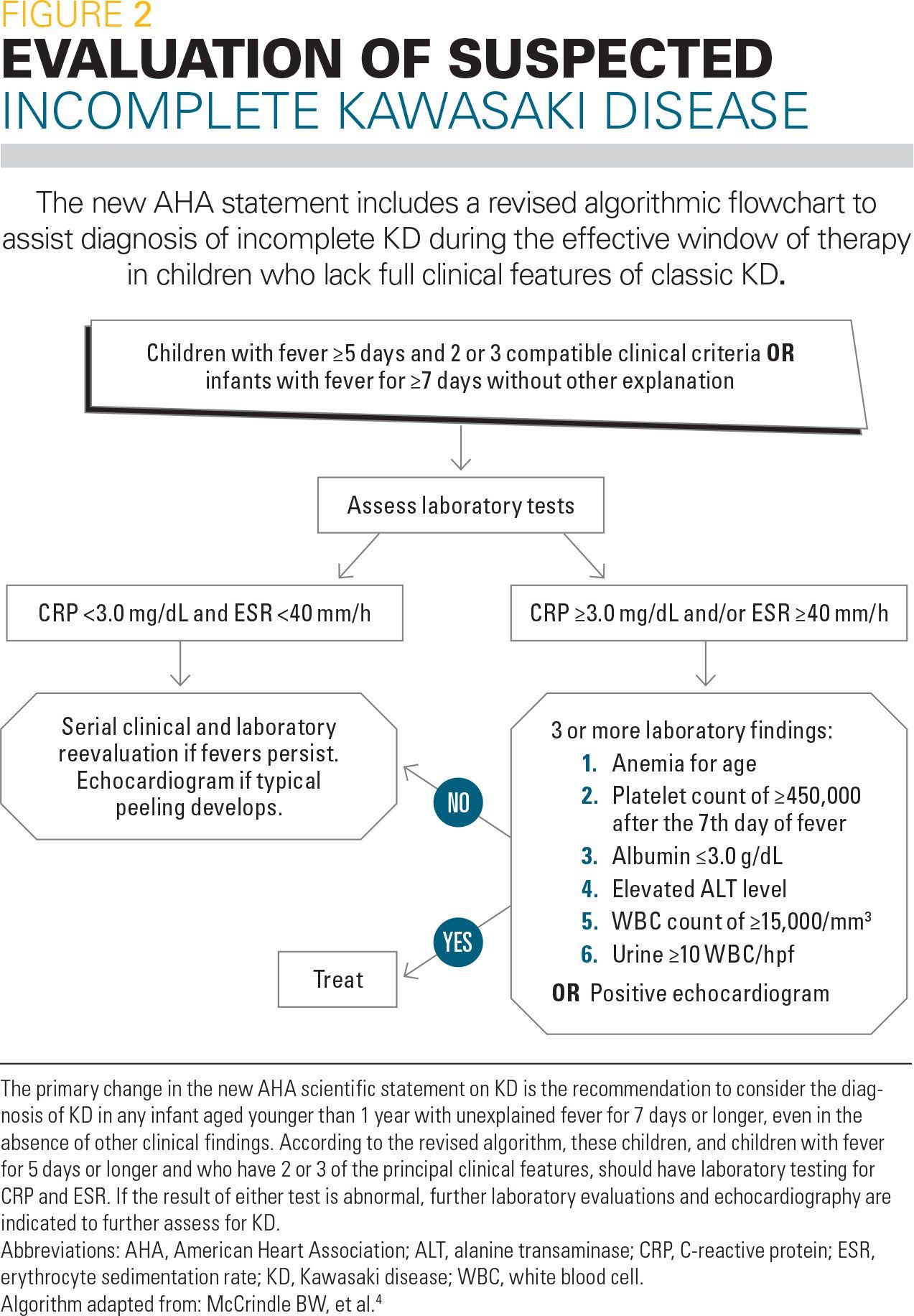
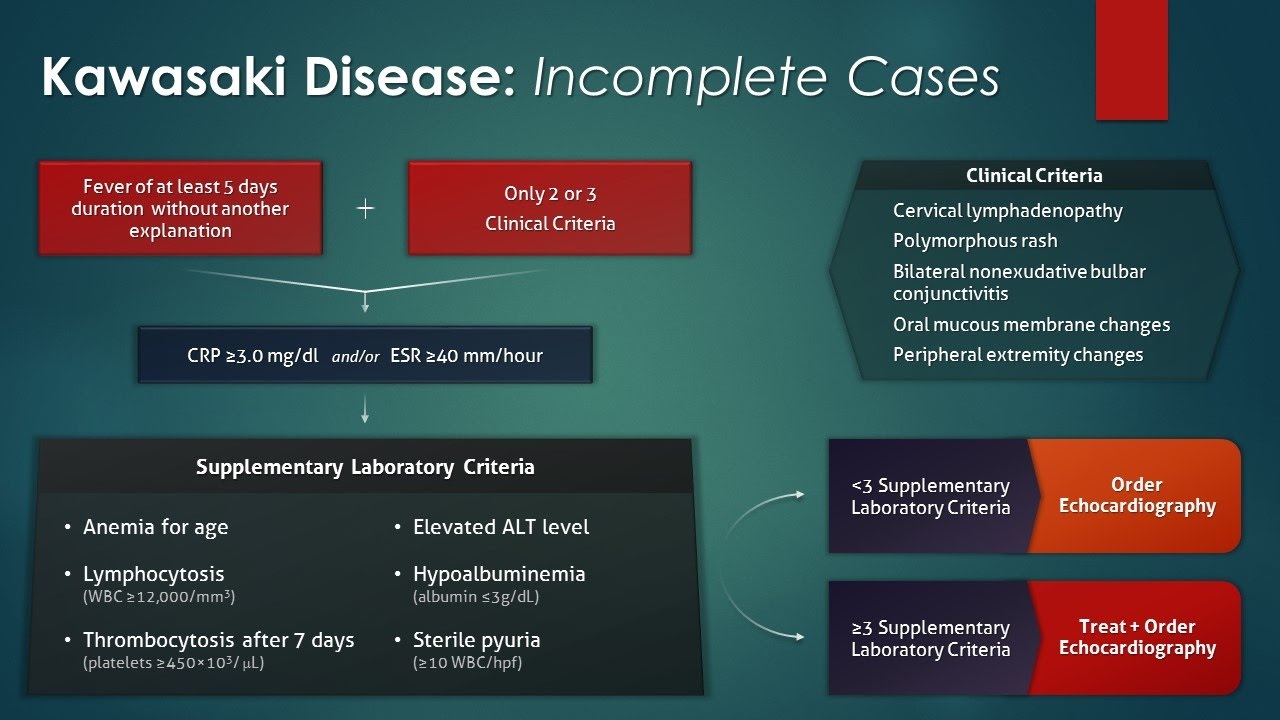
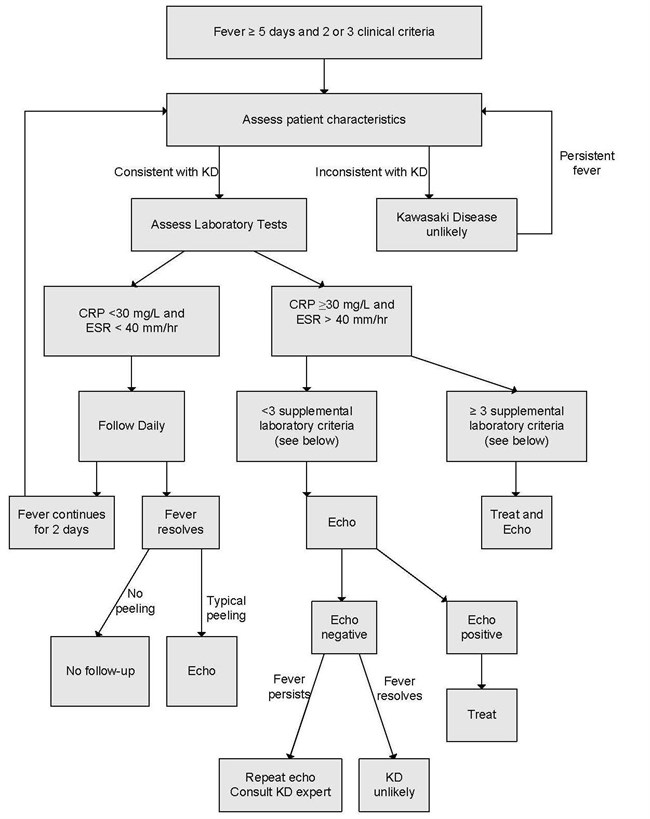
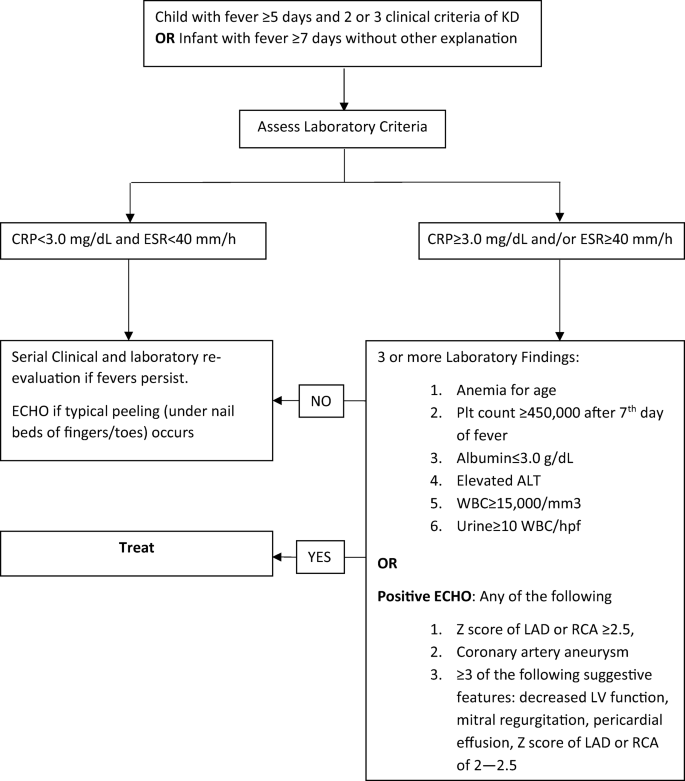
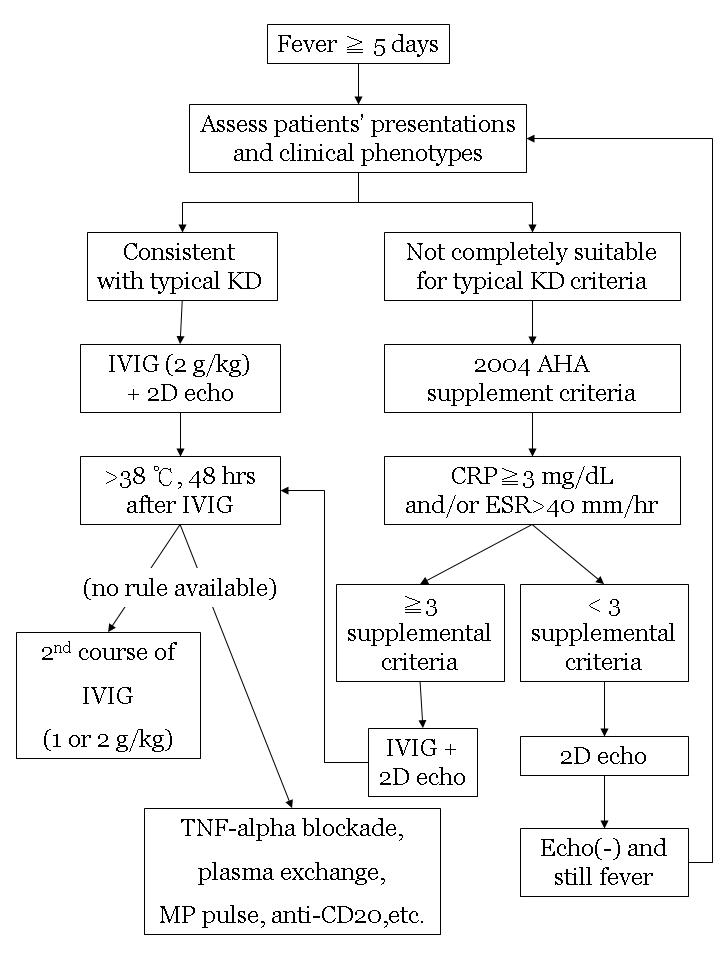
According to the Japanese criteria this criterion can only be used in cases with 4 principal symptoms2. Extremity changes swelling and or erythema peeling 5. Be aware of the diagnostic criteria of complete Kawasaki Disease KD Highest relative risk in Asian children especially Japanese ancestry Always consider incomplete KD 15-20 of cases and refer to the algorithm if concerns there are pitfalls.
Regarding incomplete atypical presentation American Heart Association guidelines state that Kawasaki disease should be considered in the differential diagnosis of prolonged unexplained fever in childhood associated with any of the principal clinical features of the disease and the diagnosis can be considered confirmed when coronary artery aneurysms are identified in such patients by. Mucosal changes injected or fissured lips injected pharynx strawberry tongue 3. 3 days of fever and strong clinical suspicion.
Incomplete Kawasaki Diseaseis when a patient presents with 5 days of fever but less than 4 clinical features. Thus strict adherence to currently accepted criteria for diagnosis of Kawasaki disease may lead to failure to recognize incomplete forms of this illness with potential sequelae of myocardial infarction or sudden death.
Awasaki disease KD is an acute self-limited fe-brile illness of unknown cause that predominantly affects children.
3 days of fever and strong clinical suspicion. Consider incomplete KD where there is prolonged fever and no alternative cause found. Assess for presence of clinical criteria at any time during current febrile illness. According to the Japanese criteria this criterion can only be used in cases with 4 principal symptoms2. Infants 6 months with unexplained fever for 7 days. These patients were seen over a 2-year period during which 22 other children were seen with Kawasaki disease with coronary artery abnormalities. Alternatively if a patient has a positive. Regarding incomplete atypical presentation American Heart Association guidelines state that Kawasaki disease should be considered in the differential diagnosis of prolonged unexplained fever in childhood associated with any of the principal clinical features of the disease and the diagnosis can be considered confirmed when coronary artery aneurysms are identified in such patients by. While the child has an incomplete set of criteria heshe has as the same risk for developing coronary artery aneurysms.
Many authors believed that this definition is too restrictive and specific7. Extremity changes swelling and or erythema peeling 5. While the child has an incomplete set of criteria heshe has as the same risk for developing coronary artery aneurysms. Many authors believed that this definition is too restrictive and specific7. Based on this suggestion a diagnosis of incomplete Kawasaki disease in analogy to the findings of complete presentation is reasonable. KD is now the most common cause of acquired heart disease in children in developed countries. If 3 or more supplemental laboratory criteria are positive a diagnosis of incomplete KD is made.




























Post a Comment for "Incomplete Kawasaki Disease Criteria"